Tulisan ini merupakan bagian dari portfolio yang saya tulis pada saat sedang mengikuti mata kuliah Design Science Education and Communication (DSEC). DSEC merupakan mata kuliah yang wajib saya ambil saat sedang melaksanakan studi di Utrecht University. Portfolio ini diberi nama Personal Design Manual (PDM). Tujuan dari tugas ini sediri adalah agar nantinya, PDM ini dapa digunakan sebagai pedoman dalam proses menciptakan desain pembelajaran. Paragraf berikut ini merupakan kalimat yang saya kutip dari Guideline dalam menulis PDM yang bisa didownload di BlackBoard Utrecht University. Semoga tulisan ini bermanfaat buat pembaca yang sedang merancang desain pembelajaran.
The aim of the task is to throughout the course develop a collection of ideas, principles, approaches and strategies that the student personally expects to be helpful in his/her future designing activities. The personal manual can be a selection of existing ideas but can also include self-developed strategies. The final result consists of the set of design principles, exemplified by concrete examples and complemented by a motivation why and how this design principle seems useful. It is hoped that the PDM document will serve as a personal guideline to start a new design activity later in the study or in a future professional career, and as such as an efficient means to access and refresh the course’s learning outcomes.
The explanation of this manual will be a part of the oral assessment. Although the manual should be a personal product, there are still general criteria that have to be met;
- Coverage; the manual summarizes the main course content
- Personal application; the manual describes which elements in the course affected the student’s own design process and how the designing experience affected the student ideas on design guidelines.
- Future guidelines; the manual describes which lessons can be learnt from the course and the design activity, that may inform the student’s future design activities.
Personal Design Manual Meeting 1
Coverage
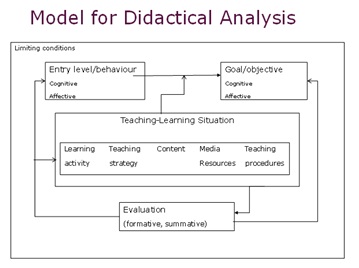
There are 4 aspects that should be concern on designing the teaching learning activity. Those aspects that also known as Model or Didactical analysis, are connected each other. They are:
1) Entry level/behaviour
Entry level/behavior that should be mention: Target group, Starting Situation and Preliminary Knowledge are well defined with information on cognitive and affective situation.
2) Goal/objective
Learning / Communication Goal describes observable learning outcomes where possible with information on cognitive and affective situation.
Based on article “How to Write Learning Objectives that Meet Demanding Behavioural Criteria” written by Dr. Bob Kizlik, there are 3 part of learning objectives; condition, behavioural verb, and criteria:
a. Conditions (a statement that describes the conditions under which the behaviour is to be performed)
Based on this aspect, the learning proposal stated the condition under which the students’ behaviour will be performed. As the chromatography problem, all of 3 objectives in the learning proposal tell about in what condition students will work, such give description; “you will” that is indicate that students are set to do something.
b. Behavioural Verb (an action word that connotes an observable student behaviour)
The word used in the objectives of the learning proposal also have to give clear instruction to students about the activity that they are going to do, such as “examine”, “compare”, “photograph”, “investigate”, “describe”, “label”, etc.
c. Criteria (a statement that specifies how well the student must perform the behaviour)
Not only have to give clear words statements, the learning proposal also have to give clear criteria such as in the chromatography problem about how many colours of ink should be investigated.
3) Teaching-Learning situation
This element consists of learning activity (activity for students), teaching strategy, content, media, resources, and teaching procedures (activity for the teacher).
4) Evaluation
There are two types of evaluation;
- The formative evaluation is an evaluation which is done by the teacher in the learning process by asking questions or asking the student to present or doing practical thing.
- The summative evaluation is an evaluation which is done by the teacher by giving written or oral test in the end of the lesson.
The complementary aspect that should also to be considered is the limiting condition. This aspect include factors that also influence the learning activities such as; the number of students, students’ prior knowledge, the time limitation, curriculum, etc.
The relation among the factor in Model for Didactical Analysis can be modelled as follows:
Learning Function:
Learning functions are answers to the question ‘why are we doing this activity?’ Therefore, the same learning function can be fulfilled by different methods.
Criteria from the MDA
- Coherence of the elements (evaluation fits the objectives, content matches the starting situation)
- Learning objectives formulated in observable behaviour
Personal Application
Based on this learning activity, I just know that there are some important aspects that should be considered in designing teaching-activity. It makes me realise that if I apply this concept in teaching in Indonesia, the teaching and learning will be more organised and effective, since every steps that I decide to do in the teaching process has its function. I also wonder how to assess whether the assessment designed (as the learning evaluation for students) fits with the learning goal. There will be a lot of tasks to do before teaching activity in the classroom such as, in order to reach the learning goal, we have to know students’ prior knowledge to make sure that the content matches with the starting situation.
Future Guideline
There are some questions that should be thought in designing:
- Which goals are to be reached?
- What is (are) the entering behavior(s)/level(s)?
- Which concepts and relations are central?
- Which teaching- and learning strategies are adequate?
- How can differences between students be addressed?
- Which resources are available?
- How can I determine whether the goals have been reached?
- What are the limiting conditions (time, number of students)?